Overview of Impaler's Minimal Engine
2023-01-12Impaler is a minimal first-person arena shooter that sells for $3. The scope and complexity of the game are relatively low compared to other titles. My approach was to build only what was necessary to power this one game. As a result, the engine is feature-poor and doesn’t compare to something like Unity or Unreal. On the bright side, these limitations helped me keep the game’s scope in check. This post will cover the major components and a few examples of their use.
High-level Organization
Impaler’s codebase is split into a hierarchy of four components: App, Menu, Game, and Engine. App represents the program as a whole and controls everything lower in the hierarchy. A component can reference the components below, but not above (e.g., Engine is unaware of the Menu). The Engine contains the most reusable parts of the codebase and will be the subject of this post.
App - window management, main loop, orchestration of other components.
Menu - everything related to the game’s user interface and navigation.
Game - game-specific code such as monsters, upgrades, and levels.
Engine - game-agnostic systems such as rendering, physics, and input.
Core (2k lines)
Core is a collection of utilities and data types commonly used by other engine components.
Visualization of various noise functions
Logging
The game is written in C, so a better logging option than printf() is needed. Instead of printf(), the game uses a great little library called log.c. This library provides logging levels (debug, warn, error) and outputs to stdout and a game.log file. The log file is key to debugging issues in the wild. Development builds have verbose logging, while production builds log sparingly. Logging is heavily used for app initialization, Steamworks, and GLFW.
Math
Math contains the floating point arithmetic used by the game. It provides vector, matrix, and quaternion math helpers (vec2, vec3, vec4, mat4x4, quat). It combines the linmath library with some of my own additions. Many of the functions are inlined as an optimization.
Input
The input system is a wrapper around GLFW input. Its purpose is to expose mouse, keyboard, and gamepad values in a game-friendly way. It handles the GLFW input callbacks and manages the engine’s internal input state.
Random
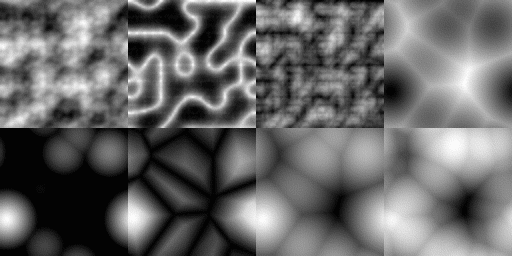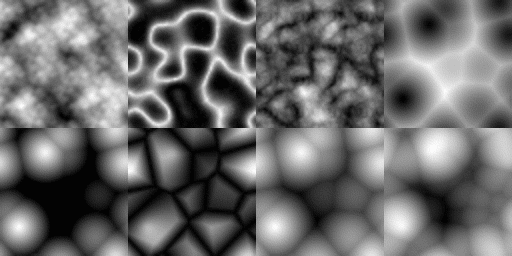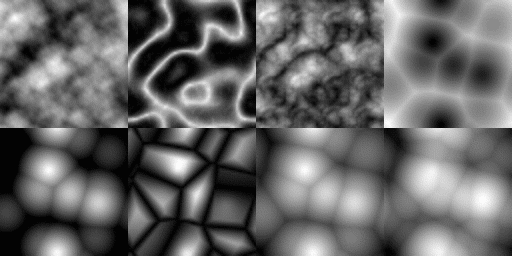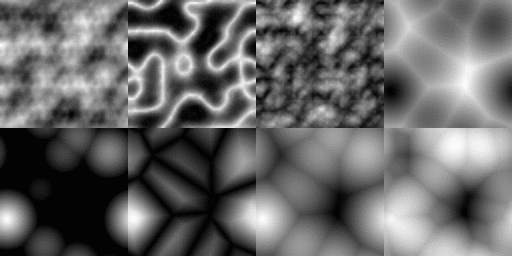
Generating random numbers is crucial for games with procedurally generated content like Impaler. Unfortunately, the stock rand() available in C has many issues. I am not an expert on random number generation, but I found this GDC video helpful. After some research, I decided to use the Xoroshiro128+ algorithm. In addition to RNG, the are helpers for sampling data from different geometries (e.g. find a random point on the inside of a sphere). There are helpers to sample from noise functions as well. Fortunately, stb_perlin exists and I only had to implement one noise function.
Color
A big part of computer graphics is working with color - often in different color spaces. In the process of creating the game, I ended up with quite a few helpers to make working with HSV and RGB colors easier. One tactic that I found particularly helpful was to create a database of “named” colors. Where possible, colors are represented as an enum that mapped to the color database. It is easier to visualize Color_reddish_pink than {1.f, 0.f, 0.5f}.
Physics (2.5k lines)
The physics system manages movement and physical interactions between objects in the game. Physics code runs on a fixed timestep in a separate loop - keeping the behavior framerate-indepedent. The system produces “events” that enable game objects to respond to what’s happening (e.g. did a player touch lava?). This is the most complex system in Impaler. It took significant effort to make it simple to use within game logic. The snippet below shows how a jump pad works (accelerating nearby objects upward).
Particles
Particles are movable volume-less points that represent things like sparks and debris. They are affected by forces such as explosions, gravity, and friction. When particles intersect other objects, they reflect off of the surface and impart a force. Particles are the foundation of the physics system.
Projectiles
Projectiles are particles optimized for fast movement and colliding with other geometry. They are used for things like bullets and grenades. When a collision occurs, the outcome is determined based on the angle of incidence, velocity, and object material. A projectile will either bounce, destruct, or penetrate through the object, depending. The math is not physically accurate, but it produces good results for gameplay purposes. When a game object is intersected, an event is created for other systems to respond to. (e.g. play a sound when a bullet ricochets)
Collision Volumes
Impaler uses axis-aligned capsules (cylinders with round ends) to represent dynamic collision geometry. They are movable, have volume, and can interact with other volumes. Collision volumes are used for characters and large game objects. Like particles, they move based on physics and react to forces in the world.
Verlet Integration
The game uses a technique called Verlet integration to control the positions and velocities of objects in the world. It’s an approximation that helps game objects behave realistically when they collide. If two monsters’ collision volumes overlap, their positions are adjusted so they no longer overlap. Then, on the next frame, velocities are recalculated based on the change in position. The Verlet integration loop is an expensive operation that involves looping through pairs of objects. It works well for slow-moving objects like the player and monsters. Events are emitted for collisions so that game logic can react later.
Ray Cast
Ray casting is a method for querying the game for intersections along a line. It answers the question: “What objects are between a start and end point?”. Ray casts consider both map geometry and collision volumes when checking for intersections.
Ray casting is used extensively
- Check if the player is standing on something
- Detect collisions for particles and projectiles
- Calculate a monster’s line of sight to the player
- Ensure explosions don’t damage objects behind walls
Event System
Since physics run in a separate update loop, an event system is used to let the physics system communicate with the game. As the physics routines run, events are enqueued track projectile intersections, collisions, and displacement of objects. This allows the game logic to consume the events and react accordingly at a later time. E.g. decrement health when the player touches lava.
Rendering (3k lines)
Impaler uses a single-pass forward renderer implemented using OpenGL. A frame is created by lighting each object as it is drawn to the output buffer. Unlike a deferred renderer, a new frame is generated without drawing an object multiple times. Forward rendering can suffer from overdraw and limited light sources. Fortunately, the game is not demanding and runs on integrated graphics. A typical frame is about ~30 draw calls.

Billboards
Much of the art in Impaler is 2D and rendered with a technique called billboarding. Essentially, each image or “sprite” is drawn on a rectangular 3D mesh that faces the viewer. Nearly everything in the game is rendered via billboards, and a frame often has 500 - 2k visible at once. A billboard management system was needed to give the game a simple API. The billboard system handles spritesheet lookups, transforming billboard geometry, and feeding the renderer. A typical call looks like this:
Camera
Like any game, a camera is needed to control what the player sees. Impaler’s camera system handles the matrix math, frustum calculations, and coordinate transformations needed for a 3D game. Most importantly, it provides an API to let the game control the camera without complicated math.
Loader
The renderer needs textures, spritesheets, and shaders to do anything interesting. The game’s resources are loaded at launch using the Loader component. The Loader interacts with the file system, parses different file types, and marshals data into the GPU. This system also compiles and links the GLSL programs. It enables the loading of OpenGL resources with a single line of code. Under the hood, it uses lodepng.
Lights
Impaler makes heavy use of dynamic lighting - things like torches and explosions are represented by point lights and provide much of the game’s eye candy. Each point light contributes to direct and specular lighting in the scene. To enable this, the fragment shader consumes a list of positions, colors, and radii representing the light sources. The light system provides the game with an easy way to manage lights without OpenGL interactions. Game code simply requests where it wants a light to exist.
Shader Management
Impaler’s shaders are fairly complex and have a large number of inputs. As a result, there is a system that simplifies locating, caching, and feeding shader uniform variables. This component takes a configuration struct and manages OpenGL accordingly. It controls the lighting and visual effects like soft particles and parallax mapping.
Meshes
The last major piece of the renderer is functionality for managing 3D meshes. While 2D in presentation, billboards still need to be represented by 3D geometry.
This system is mostly a collection of utilities that:
- Manage dynamic geometry such as billboards
- Recalculate normals
- Sort geometry for alpha blending
- Assign UV coordinates based on spritesheet lookups
- Manage per-vertex metadata that is passed to the vertex shader
Audio (1k lines)
The audio system encapsulates the functionality for loading and rendering spatialized sounds and music. A great library called miniaudio does much of the heavy lifting here. Like the other components, the goal was to provide the game with a simple API without sharp corners. Below is a short snippet of how a sound is played:
Spatializer
The spatializer helps render the game’s audio in a realistic way. It handles the calculation of:
- Distance-based volume attenuation
- Sound occlusion based on ray casting (e.g. sounds behind a wall are quieter)
- Stereo panning based on the position and orientation of the listener
- Pitch shifting when the game is in a “slow motion” gameplay segment
Once the spatializer determines how a sound should be rendered, it calls the appropriate miniaudio functions to update the active audio source.
Manager
Like most games, a finite number of sounds can play concurrently. The audio manager helps prioritize which sounds should play (or be recycled for higher-priority sound events). It also chooses which variation should play when multiple sound instances exist (e.g. explosion_1.wav, explosion_2.wav, etc.). One of the more interesting tasks was creating an API for managing looping sounds that persist for the lifetime of an object. When a looping sound is “retained” by a game object, it will continue to play. Otherwise, the manager will know to end the loop and recycle it into the pool.
Modules (500 lines)
Modules are higher-level systems composed of multiple engine components. The particle system module combines both rendering and physics, for example. There are only two modules today, but this category will grow as new features are added to the game.
Particle Cloud
Particle clouds power the game’s visual effects, such as explosions and sparks. In Impaler, they are implemented as billboards attached to physics particles. First, billboards are arranged in 3D space to create the illusion of volume. Then, physics is applied to the billboards to achieve the desired visual effect (rising smoke, bouncing sparks, etc.). Particle effects contribute to overdraw, but they look nice and are simple to create. Creating a particle cloud looks something like below:
Trail Renderer
Trails renderers are used to draw things like smoke trails and fireballs. Trails are strips of triangles that follow a moving object. The rocket smoke in the next screenshot is a good example of its use.

Wrapping Up
The systems covered above are suitable for making a small game like Impaler. However, they would not support other games very well. Only commercial engines will be extensive enough to support any type of game. I plan to cover a more technical graphics topic in the next post.
